Explaining "Process Definition Introduction" Video
Published 29-12-2022 by Hector Tessari - Kuflow Team

Credits: Hector Tessari
Welcome to our blog! KuFlow, is a platform that allows you to define and manage processes in various ways.
A Process Definition in KuFlow represents a workflow, or a series of interconnected tasks. It consists of various parameters, and can be controlled by different engines such as the KuFlow Engine (based on Temporal.io), APIs and Webhooks, our Diagram Tool, that could be used for simpler processes, or even no engine at all – in this case, the sequence of tasks is defined by the end-user at runtime.
For processes controlled by the KuFlow Engine, you must define which application will manage the workflow, as well as the identifiers for the Workflow Application and Task queue. These identifiers are used for communication between KuFlow and the workers participating in the workflow.
Metadata allows you to use global data at the workflow level, which can be used for searches and visualization. User Actions enable the definition of special actions at the process level, giving you more flexibility and power in your workflows – for example, you can create a new task on demand, start a related process, or download a file.
Permissions in KuFlow allow you to determine what each user is able to do, either through specific user permissions or group permissions. You can define Initiators of a process, which means a process can only be initiated by certain users or by all members of your organization. Process managers, who are able to monitor all executions of a workflow and their related information, can also be defined. The Administrator permission allows certain users to make changes to the Process Definition.
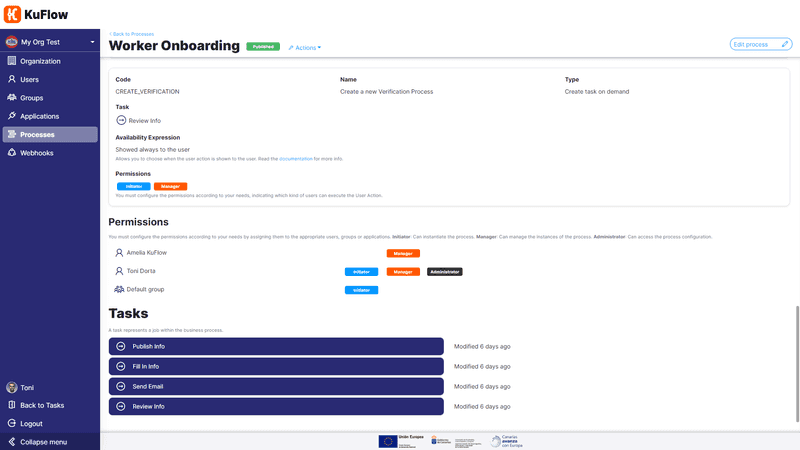
A Workflow consists of a list of tasks, which is simply a definition of the tasks and doesn't determine their order of execution. The task flow can be determined in various ways, depending on the process definition's engine – for example, if it is based on the KuFlow Engine, the application worker determines the flow of tasks. If it is defined using the Diagram Tool, KuFlow follows the order stipulated in the diagram. If no workflow engine is defined, the order is chosen at runtime by the end-user.
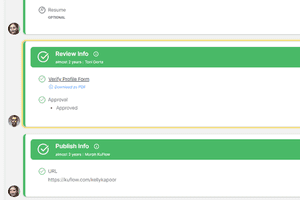
Each task is defined with a description and an identifier, and has a list of candidates – users who can claim and perform the task. For human tasks, you can define specific users or groups of users as candidates, who will have the option to claim the task in order to perform it. For automatic tasks, you can define which application will assume and execute the task.
Tasks can also have various elements, which are used for interacting with users, asking and displaying information. These elements can be of different types, and can be mandatory, read-only, or multi-valued. validations can be defined to ensure correct data entry.
Here is a video that we have made for you that explains everything mentioned above.
Our recommendation for you is to try KuFlow by creating a free account and finding out for yourself.
For more information, visit our technical documentation and our video tutorials.